- Who We Are
- Updates & News
- Standards
- Software Tools
- Network Studies
- Community Forums
- Education
- New To OHDSI?
- Community Calls
- Past Events
- 2024 India Symposium
- 2024 Europe Symposium
- 2024 Thailand Tutorial
- 2024 Japan Tutorial
- 2024 DevCon
- 2024 Phenotype Phebruary
- 2023 Global Symposium
- 2023 APAC Symposium
- 2023 Europe Symposium
- 2023 SOS Challenge
- 2023 DevCon
- 2023 Phenotype Phebruary
- 2022 Global Symposium
- 2021 Global Symposium
- 2020 Global Symposium
- ALL Past OHDSI Events
- Workgroups
- 2024 ‘Our Journey’ Annual Report
- Current OHDSI Events
- Support & Sponsorship
- CBER Best Seminars
- 2024 Global Symposium
- 2024 APAC Symposium
- Github
- YouTube
- Newsletters
Vaccine Surveillance Method in Observational Data May Generate High Number Of False Positives
Worldwide efforts to promote vaccination require reliable evidence about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to build trust in their use. Regulators and other public health agencies play a critical role in generating and synthesizing evidence across an array of data sources as part of a collective public health infrastructure.
One desired component of that system is the use of observational data, such as de-identified electronic health records and administrative claims, to conduct analyses that can identify true adverse events of vaccines as quickly as possible, while simultaneously reducing the chance that analyses generate false positive findings that may stimulate unnecessary worry.

In this context, understanding the reliability of study designs in vaccine surveillance systems is important to ensure that evidence is appropriately used by all stakeholders.
Historical comparator designs, which compare background rates of events in a general population versus observed rates amongst a vaccinated cohort, have been regularly used by regulators and other vaccine safety researchers. Those studies may generate a high number of false positives, according to a recent study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology. The paper, which studied the methods used for surveillance of the H1N1, flu, and other recent vaccines, highlight a need to further evaluate study design in this critical time of COVID-19 vaccine surveillance.
Age-sex adjustment and empirical calibration were among the measures used to produce more reliable surveillance monitoring findings, according to the study “Bias, Precision and Timeliness of Historical (Background) Rate Comparison Methods for Vaccine Safety Monitoring: An Empirical Multi-Database Analysis” led by Xintong Li, a DPhil candidate at the University of Oxford, and supported by the OHDSI and EHDEN open science communities.
A Common Method Of Surveillance
Regulatory agencies have previously used the method of historic comparisons, a design that focuses on the rate of adverse events following immunization and compares it to the expected incidence rate within a general population.
“This is a method that relies on the comparison of historical data, which is then compared to post-vaccine events,” said senior author Daniel Prieto-Alhambra MD MSc PhD, Professor of Pharmacoepidemiology at the University of Oxford. “Vaccinated people are however not always comparable to the general population. They tend to be older and more vulnerable than the average citizen. Therefore, the comparison of post-vaccine versus historical rates tends to detect false positives.”
The study team observed these false positives by introducing 93 negative controls, which are exposure-outcome pairs where the exposure is believed to not cause or prevent the outcome, as well as positive controls on different sets of vaccinated patients (H1N1, flu, Varicella-Zoster, HPV) between September 2009 and December 2018 across four databases. Analyses showed tendencies to overestimate risks, in some cases by as much as 100%.
Efforts to improve study design included age and sex adjustment and anchoring background rates around a healthcare visit, both of which reduced the false positive error rate. Empirical calibration had an even greater impact on false positive error rate, though it led to an increase in false negatives.
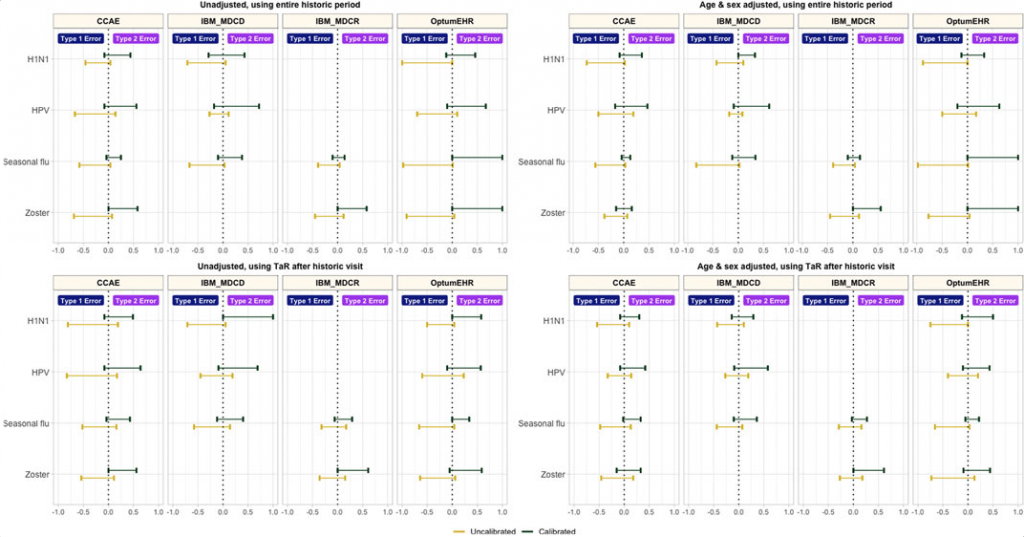
Type 1 and type 2 error before vs after empirical calibration
The Path Towards Generating Trust
Continued work on the process of vaccine safety surveillance is crucial, as generating accurate evidence is the clearest path to creating trust within the general public.
“Studying historical comparisons is one of many alternative approaches that could be used for vaccine surveillance,” said Martijn Schuemie, Research Fellow in Epidemiology Analytics at Janssen Research and Development, who has led OHDSI’s EUMAEUS (Evaluating Use of Methods for Adverse Event Under Surveillance) study, which aims to systematically evaluate methods for (safety) surveillance of vaccines. “We hope this methodological work helps the broader community understand which approaches may be most effective to support global safety efforts.”
“Methodological research on vaccine safety methods is now more important than ever before,” Prieto-Alhambra said. “We need to make sure that the research we do is reliable, and to avoid false positives and negative findings.”
OHDSI (Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics) is an open-science community dedicated to the mission of improving health by empowering a community to collaboratively generate the evidence that promotes better health decisions and better care. OHDSI currently collaborates with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide support to the Biologics Effectiveness and Safety (BEST) program, which was launched by the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) in 2017.
The lead research team, primarily comprised of OHDSI personnel from Columbia University, UCLA, and Northeastern University, provides support to the BEST system in its mission to conduct safety and effectiveness surveillance of biologic products, including vaccines.
Similarly, the EHDEN (European Health Data and Evidence Network) Consortium has generated real-world evidence that has been shared with the European Medicines Agency. Prieto-Alhambra is hopeful that this study will cause such agencies to consider the currently accepted methods used for vaccine surveillance.
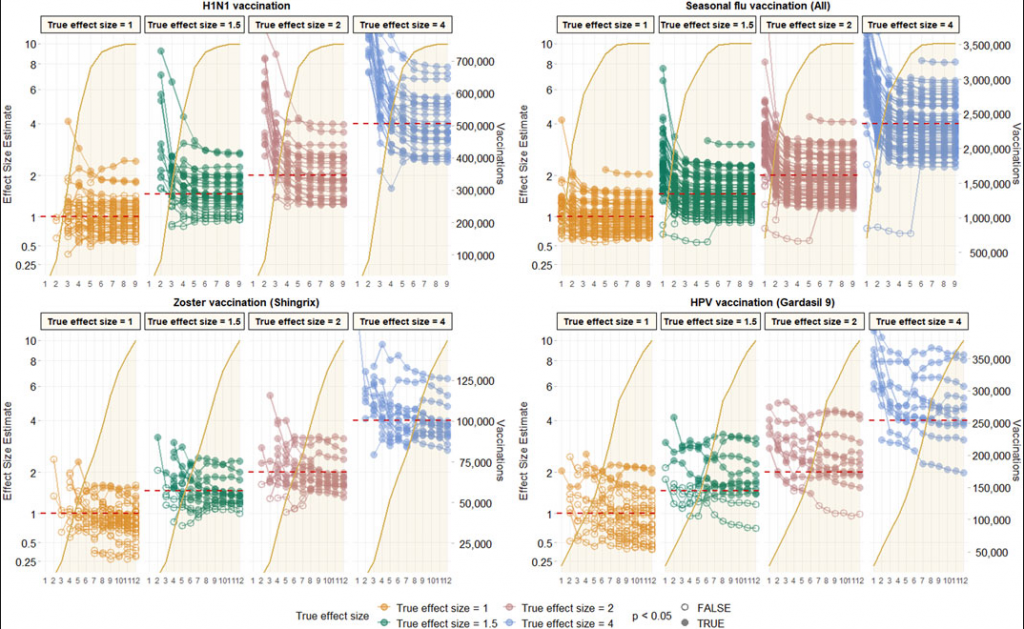
Observed effect size for negative control outcomes (true effect size = 1) and positive control outcomes (true effect size = 1.5, 2 and 4) [left Y axis] and vaccine uptake [right Y axis and shaded orange area] over time in months [X axis] based on analyses of CCAE data with age-sex adjusted, and using the visit-anchored time-at-risk definition.
“The most important learning is that any signal identified using historical comparison methods has a high probability of being a false positive, and should be treated as such until confirmed in more robust studies/analyses,” he said.
About This Study
The study “Bias, Precision and Timeliness of Historical (Background) Rate Comparison Methods for Vaccine Safety Monitoring: An Empirical Multi-Database Analysis” was published Nov. 24, 2021, in Frontiers of Pharmacology.
Authors: Xintong Li, Lana YH Lai, Anna Ostropolets, Eng Hooi Tan, Paula Casajust, Thamir M. Alshammari, Talita Duarte-Salles, Evan P. Minty, Carlos Areia, Nicole Pratt, Patrick B. Ryan, George Hripcsak, Marc A. Suchard, Martijn J. Schuemie, Daniel Prieto-Alhambra
Funding: UK National Institute of Health Research (NIHR), European Medicines Agency, Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 (806968), US Food and Drug Administration CBER BEST Initiative (75F40120D00039), and US National Library of Medicine (R01 LM006910). Australian National Health and Medical Research Council grant GNT1157506.
